Know All About Histamine
Histamine is a natural compound that is present within the human body and directs a large number of important functions in day-to-day life. The adaptability of Histamine positions it as a conductor in the intricate symphony of human physiology. To clearly understand Histamine, it is essential to understand the meaning and instances of physiological activities.
Physiological activities mean various processes and functions that take place within the human body at the cellular, tissue, organ, and systemic levels. These activities are vital for the crucial maintenance of life and the proper functioning of the body. The well-being of an individual heavily depends upon proper physiological activities and in the absence of which a list of health issues arises.
Key Roles of Histamine:
Apart from these crucial functions, it is a multifaceted performer ensuring the seamless functioning of various physiological processes ranging from neurotransmission to digestion, immune response, and much more.


What is Histamine Sensitivity?
Understanding Histamine Sensitivity
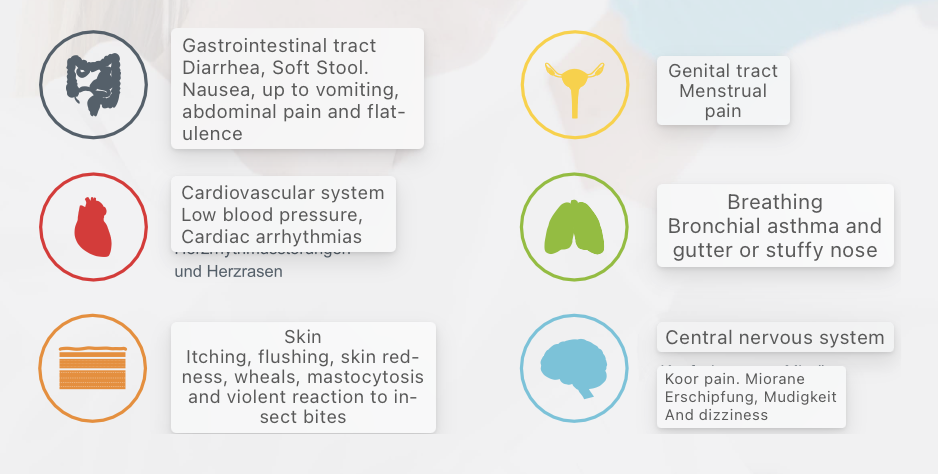
Excess of anything causes problems and so does histamine. When there is an excess of Histamine in the body it tends to cause side effects that may get serious sometimes. The reactions caused by histamine are mostly similar to those of food allergies, however, with the advancements in the healthcare industry, it is feasible to understand the hidden causes too. Histamine sensitivity is detectable and it is quite different from regular allergies that hamper your normal routine. Conditions like "idiopathic" urticaria and angioedema (hives) show us that histamine sensitivity is more than just a symptom. It's its own separate health concern that requires special attention and care.